Analysis of Anthropic's internal data reveals software engineering accounts for approximately 50% of AI agent tool calls, highlighting significant untapped potential in healthcare, finance, and other sectors where adoption remains low.
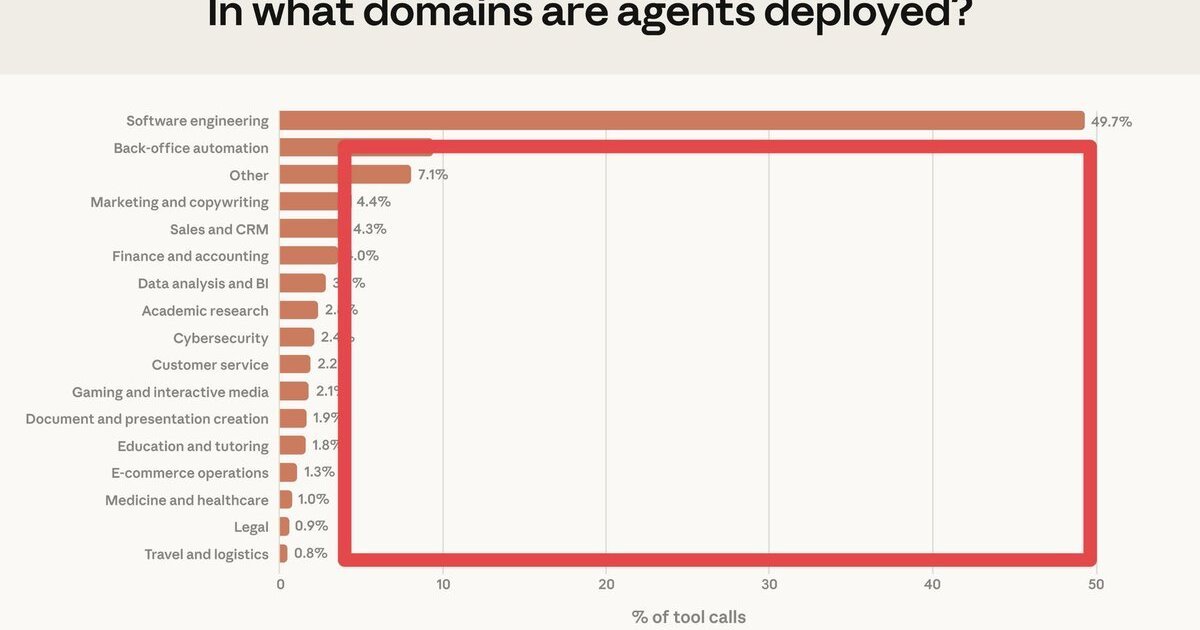
Internal metrics from Anthropic reveal a stark imbalance in AI agent adoption: nearly half of all tool calls across its Claude-based agent ecosystem target software engineering tasks. According to analysis by Garry Tan published on Garry's List, this distribution exposes a market gap where founders continue overlooking opportunities in verticals like healthcare documentation, financial analysis, and legal contract review.
The data indicates that code generation, debugging, and API integration tasks constitute the dominant use case for AI agents today. This aligns with Anthropic's public releases like Claude Code, which specifically targets programming workflows. The concentration persists despite agents technically being capable of handling diverse tasks through function calling and tool use.
What's substantively new here isn't the existence of coding-focused agents—tools like GitHub Copilot have existed for years—but the quantified evidence of how dramatically this single vertical overshadows others. The remaining 50% of tool calls fragment across dozens of industries, with no single non-engineering vertical exceeding 5-7% adoption. This fragmentation suggests most domains remain greenfields with minimal organized development efforts.
Several factors drive this imbalance:
- Tool maturity: Software engineering benefits from structured languages, test suites, and version control systems that provide clear success metrics for AI outputs
- Data availability: Public code repositories offer abundant training data unavailable in regulated domains like healthcare
- Early adopters: Developers naturally experiment with tools automating their own workflows first
Yet the limitations of this concentration are becoming apparent. When Anthropic recently launched Claude Code Security—an automated vulnerability scanner—its impact on cybersecurity stocks demonstrated how quickly agent capabilities can disrupt adjacent markets. Similar opportunities exist in neglected sectors:
- Clinical documentation: Automated SOAP note generation from doctor-patient dialogues
- Financial compliance: Real-time SEC filing analysis for asset managers
- Industrial maintenance: Predictive equipment failure alerts from sensor logs
Barriers persist in non-software domains, including regulatory hurdles, data silos, and complex domain-specific validation requirements. Anthropic's data also reflects its user base—primarily technical early adopters—meaning actual enterprise adoption patterns may differ. However, the 50% benchmark provides a clear indicator of where the market isn't looking.
As Tan notes, this distribution isn't a warning but a roadmap. Founders building beyond the crowded software tools space face less competition for talent, partnerships, and market share. The challenge lies in solving domain-specific integration and trust issues that current platforms don't address—precisely where sustainable differentiation emerges.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion