Discover how GitHub Actions enables fully automated merging of Dependabot security patches, reducing maintenance overhead while enforcing CI/CD quality gates. This workflow transforms dependency management from reactive chore to proactive safeguard – but demands robust testing foundations.
The Dependency Maintenance Dilemma
Security patches remain one of software development's most persistent challenges. While platforms like GitHub provide automated vulnerability alerts through Dependabot, teams often struggle with the operational burden of manually reviewing, testing, and merging dozens of patch PRs. This friction frequently delays critical updates, leaving systems exposed.
Will Larson's recent experiment reveals an elegant solution: Configuring GitHub Actions to autonomously approve and merge Dependabot pull requests. The approach leverages existing CI/CD safeguards as quality gates, turning dependency management into a self-regulating system.
How Automated Merging Works
The automation hinges on a carefully crafted GitHub Actions workflow:
# Automatically approve and merge Dependabot PRs
name: Dependabot auto-merge
on: pull_request
permissions:
contents: write
pull-requests: write
jobs:
dependabot:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: github.event.pull_request.user.login == 'dependabot[bot]'
steps:
- name: Dependabot metadata
id: metadata
uses: dependabot/fetch-metadata@v2
with:
github-token: "${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}"
- name: Approve Dependabot PR
run: gh pr review --approve "$PR_URL"
env:
PR_URL: ${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url }}
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Merge patch/minor updates
if: steps.metadata.outputs.update-type == 'version-update:semver-patch' || steps.metadata.outputs.update-type == 'version-update:semver-minor'
run: gh pr merge --auto --squash "$PR_URL"
env:
PR_URL: ${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url }}
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
Key safeguards in this workflow:
- Selective Activation: Only triggers for Dependabot-originated PRs
- Update Scoping: Auto-merges only patch/minor updates (excluding major versions)
- CI Enforcement: Respects repository branch protection rules and required status checks
 Example workflow configuration enabling automated merging (Source: lethain.com)
Example workflow configuration enabling automated merging (Source: lethain.com)
Implementation Walkthrough
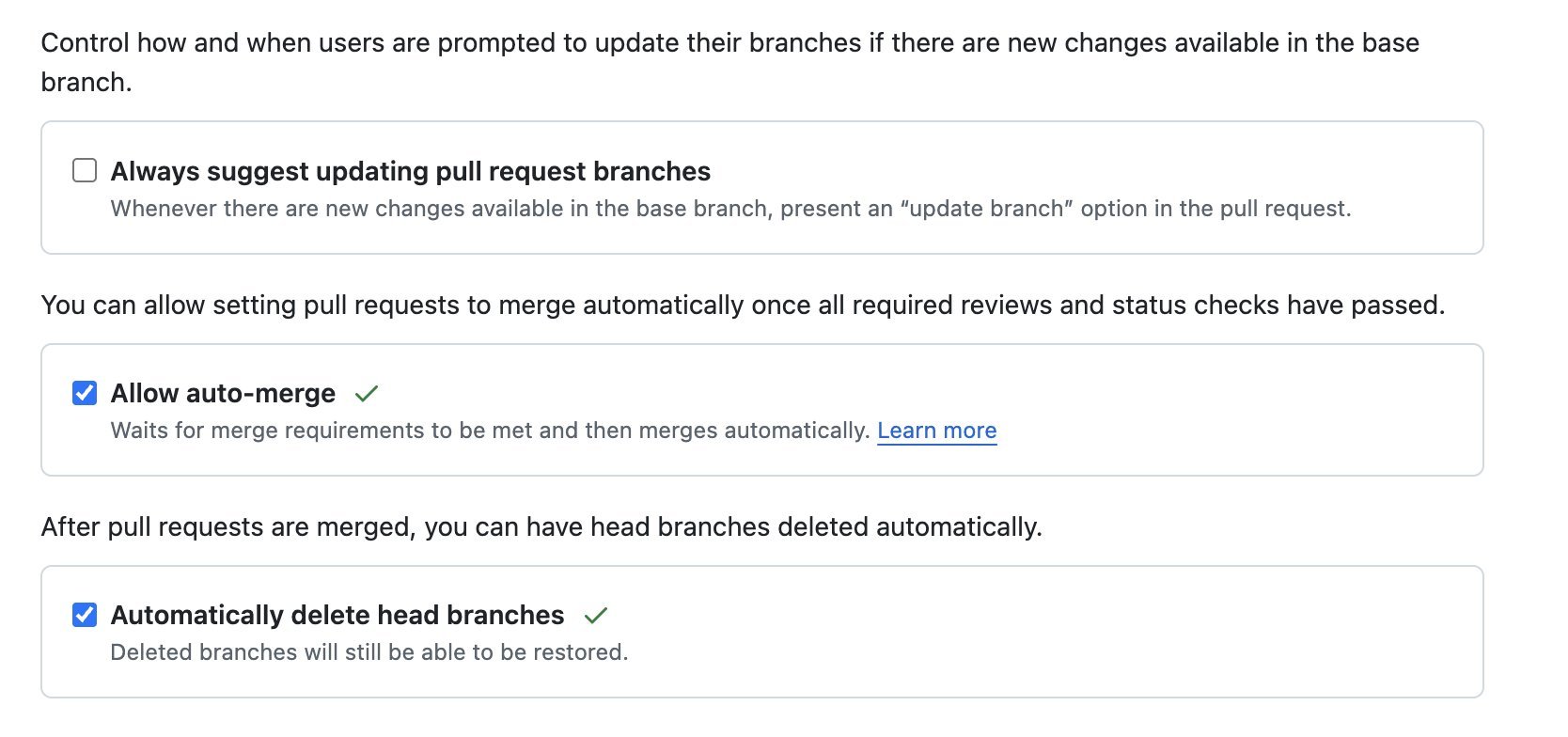
Enable Repository Settings: Activate "Allow auto-merge" in repository settings while maintaining branch protection rules
 Auto-merge configuration in GitHub repository settings
Auto-merge configuration in GitHub repository settingsEstablish Quality Gates: Implement mandatory status checks for linting, testing, and type safety in CI/CD pipelines
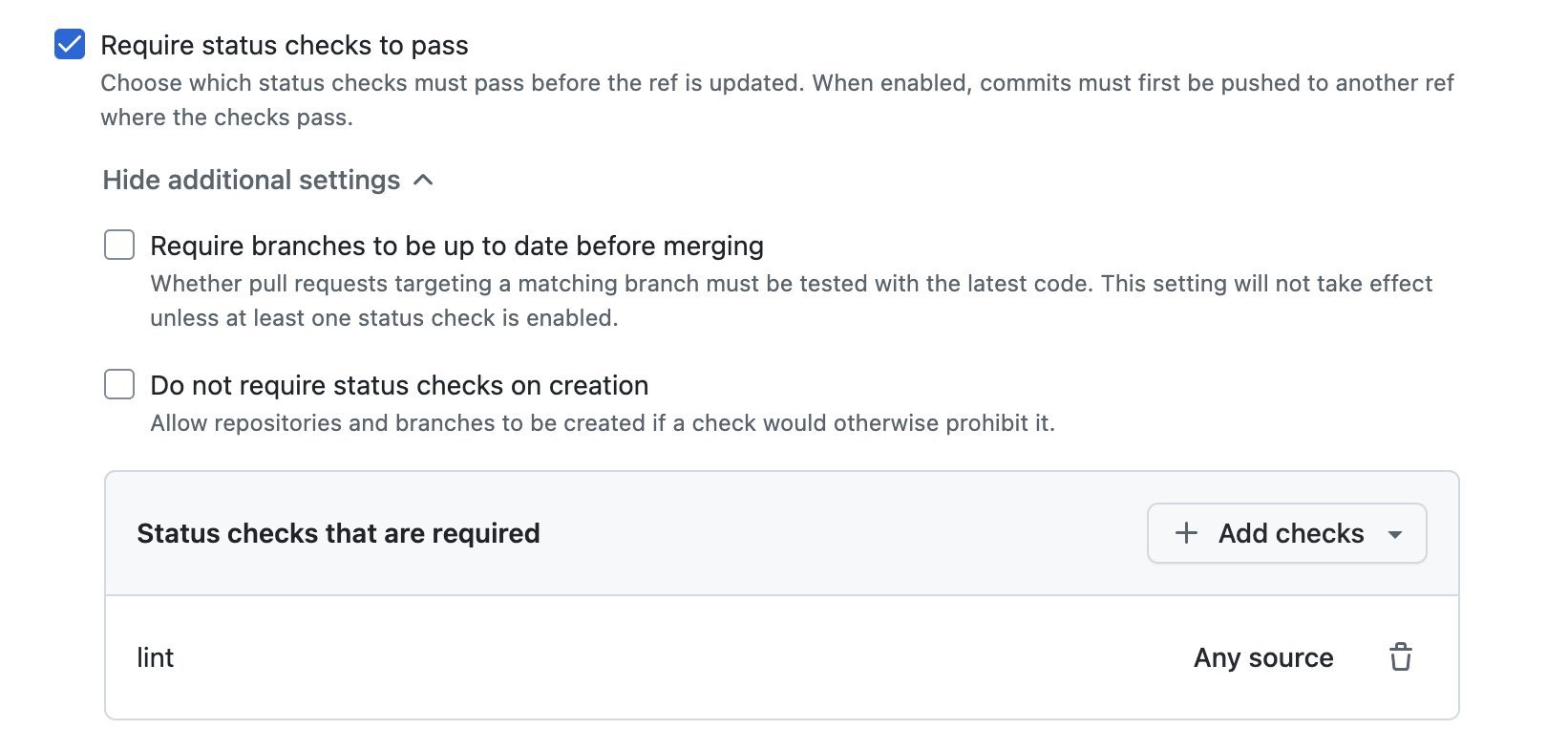 Required status checks act as safety nets for automated merges
Required status checks act as safety nets for automated mergesConfigure Dependabot: Enable security updates in repository settings (default configurations often suffice)
The CI/CD Imperative
This automation's effectiveness directly correlates with test suite quality. As Larson notes:
"If you have great CI/CD that runs blocking linting, typing and tests, then this works particularly well. If you don’t, this will be an effective mechanism to get you there after traversing a small ocean of tears."
The workflow transforms dependency management into a forcing function for engineering excellence. Teams gain rapid security patching while technical debt surfaces through broken auto-merges – creating natural pressure to improve test coverage and automation reliability.
Beyond Automation: Shifting Left on Security
This approach exemplifies modern DevSecOps philosophy: integrating security practices directly into developer workflows. By reducing friction for routine updates, teams can redirect human oversight toward architectural risks and novel vulnerabilities. The automated pipeline becomes both shield and catalyst – securing dependencies while continuously validating code health.
Source: Implementation details adapted from lethain.com

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion