GateBooster addresses the gap in GATE exam preparation by providing a clean, distraction-free CBT simulation that mirrors the actual testing environment, built with modern web technologies while overcoming significant production deployment challenges.

The Problem: Authentic Exam Simulation Gap
Most GATE preparation platforms fail to replicate the actual Computer-Based Test (CBT) environment crucial for effective exam readiness. Common issues include:
- Visual clutter and unnecessary UI elements
- Distracting advertisements and popups
- Poor navigation flow mismatched with actual GATE interfaces
- Inadequate time pressure simulation
This creates a significant gap since the actual GATE exam emphasizes:
- Minimalist interface design
- Precise time management
- Efficient question navigation
- Uninterrupted focus
GateBooster's Solution Approach
GateBooster implements a production-ready architecture focused exclusively on CBT simulation:
Core Technical Components:
- Frontend: Next.js (App Router) with TypeScript and Tailwind CSS, deployed on Vercel
- Backend: Fastify-based Node.js API server hosted on Railway
- Authentication: JWT with HttpOnly/Secure/SameSite cookies
- Database: Structured storage for users, exams, and responses
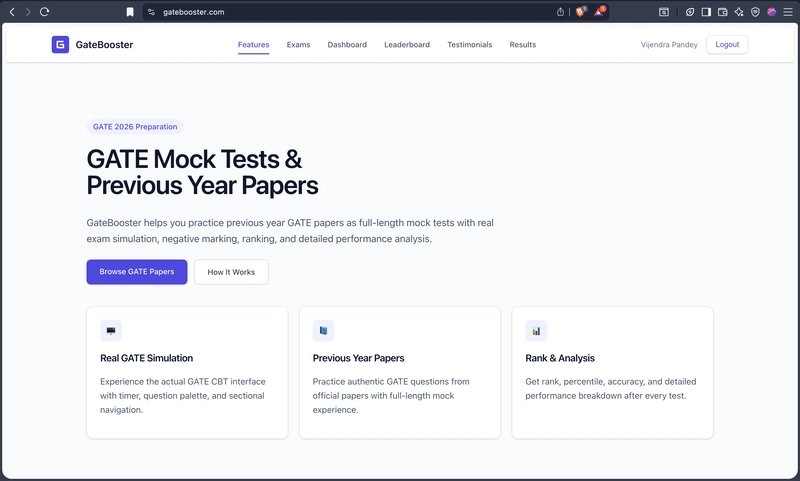
Key Functional Features:
- Full-length timed exams with auto-submission
- Realistic question palette with status indicators
- Section-based navigation mirroring actual GATE workflow
- Post-test performance analytics
- Zero-advertisement interface
Production Deployment Challenges
The transition from local development to live environment surfaced critical distributed systems challenges:
Cross-Domain Authentication Issues
- Cookie conflicts between Vercel (frontend) and Railway (backend) subdomains
- Inconsistent SameSite policy enforcement across browsers
- Debugging silent authentication failures requiring Chrome DevTools' Application tab inspections
CORS Complexities
- Preflight request failures for credentialed requests
- Dynamic origin configuration based on environment (dev vs prod)
- Security-vs-functionality tradeoffs in Access-Control-Allow-Origin settings
Environment-Specific Failures
- Discrepancies between local environment variables and cloud provider configurations
- Build-time vs runtime variable injection differences
- Third-party service API key permission mismatches
SEO Implementation Hurdles
- Dynamic sitemap generation for exam pages
- Search Console verification delays
- Indexing priority management for public vs authenticated routes
Architectural Tradeoffs
| Design Choice | Benefit | Compromise |
|---|---|---|
| JWT Cookies | Stateless auth simplifies scaling | Requires strict cookie policies |
| Multi-cloud Deployment | Optimal performance for global users | Cross-origin complexity |
| Monolithic Backend | Faster initial development | Scalability limitations at high load |
| SSR for SEO | Public page discoverability | Increased server resource consumption |
Lessons from Production
- Environment Parity: Maintain identical configuration management across dev/staging/prod
- CORS as Feature: Implement automated CORS configuration tests in CI pipeline
- Observability Gap: Added logging middleware for auth flow visibility
- Cookie Consistency: Standardized cookie settings across all environments
Conclusion
GateBooster demonstrates that shipping production systems requires solving problems beyond core functionality. The platform now serves real users at gatebooster.com, providing authentic CBT simulation while continuously evolving based on user feedback. The project highlights how production deployments expose distributed systems challenges rarely encountered during local development, particularly around cross-domain security, environment consistency, and third-party service integration.
For GATE aspirants, it offers exam-realistic practice. For developers, it provides concrete examples of overcoming deployment hurdles in modern web applications.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion