GitHub introduces a citation-based memory system for Copilot agents that enables cross-workflow learning while maintaining accuracy through real-time verification.

GitHub's vision for Copilot as an interconnected agent ecosystem spanning coding, review, security, and deployment requires overcoming a fundamental limitation: the stateless nature of current AI interactions. Traditional AI coding assistants treat each session as a blank slate, forcing users to repeatedly provide context. To address this, GitHub has developed an agentic memory system that allows Copilot components to retain and share validated knowledge across sessions and workflows.
The Core Challenge: Valid Knowledge Over Time
Unlike conventional databases, codebases exist in constant flux across branches and versions. A logging convention observed today might be deprecated tomorrow, or an API synchronization pattern might only exist in an unmerged feature branch. Storing static "facts" risks propagating outdated or incorrect information. Early explorations with offline curation systems proved impractical at GitHub's scale due to engineering complexity and LLM costs.
GitHub's solution: Shift validation from write-time to read-time using a citation-based approach. Memories are stored as tuples containing:
- The observed pattern (e.g., "API version must match between client SDK/server routes/documentation")
- Citations pointing to specific code locations (file paths + line numbers)
- A reason explaining why the pattern matters
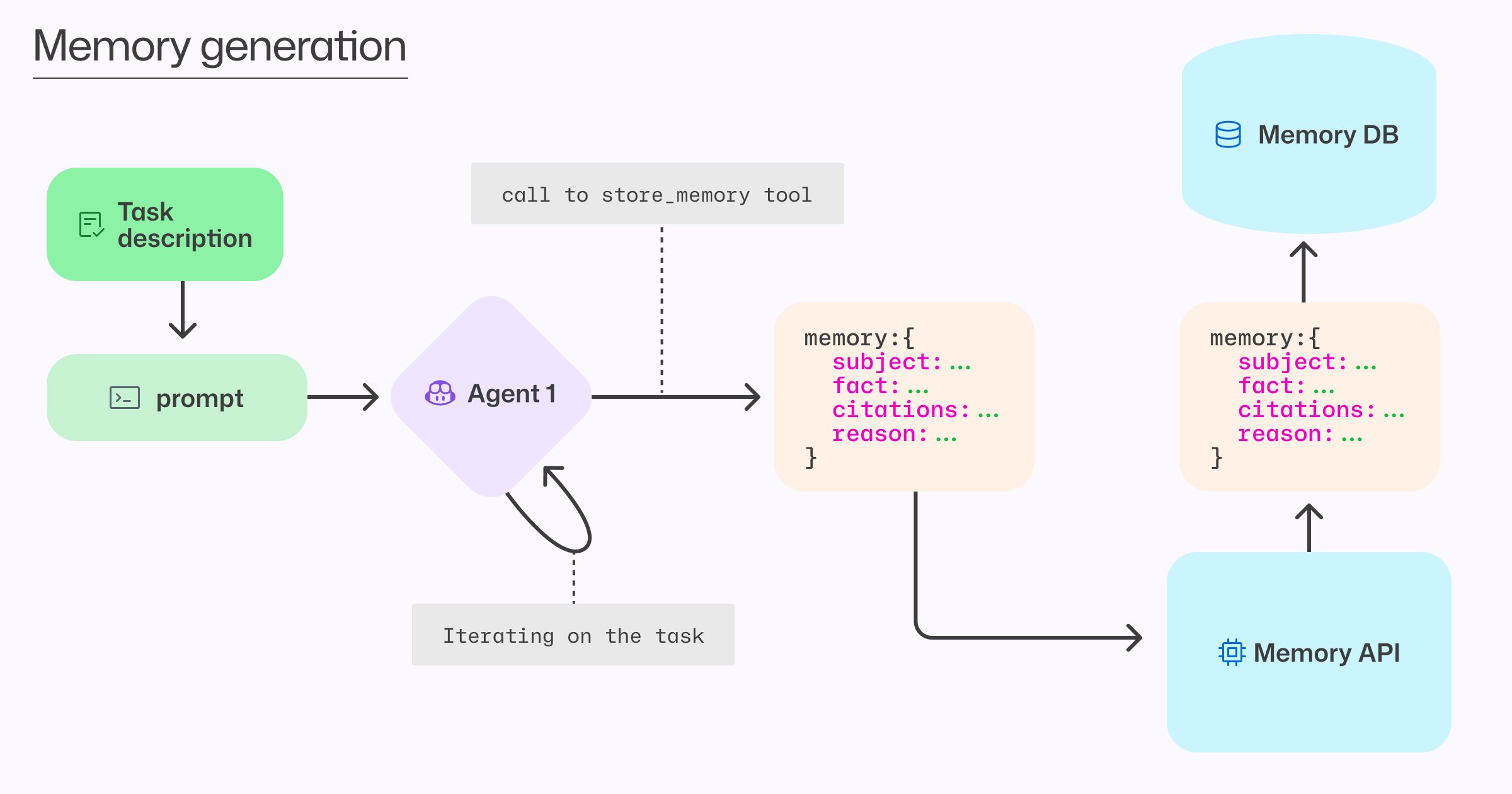 How Copilot agents store learnings worth remembering during task execution
How Copilot agents store learnings worth remembering during task execution
Implementation Mechanics
Memory Creation: Agents invoke a dedicated tool during task execution when they discover impactful patterns. For example:
- During code review, Copilot notices API version strings synchronized across three files
- It stores this observation with citations to each location
- Includes a reason: "Version mismatches cause integration failures"
Memory Retrieval: At task initiation, relevant memories are fetched for the repository. Future enhancements will add semantic search and priority weighting.
Verification: Before applying any memory, agents perform real-time checks:
- Validate citation targets still exist
- Confirm current code aligns with the memory
- If discrepancies exist, agents can update or deprecate the memory
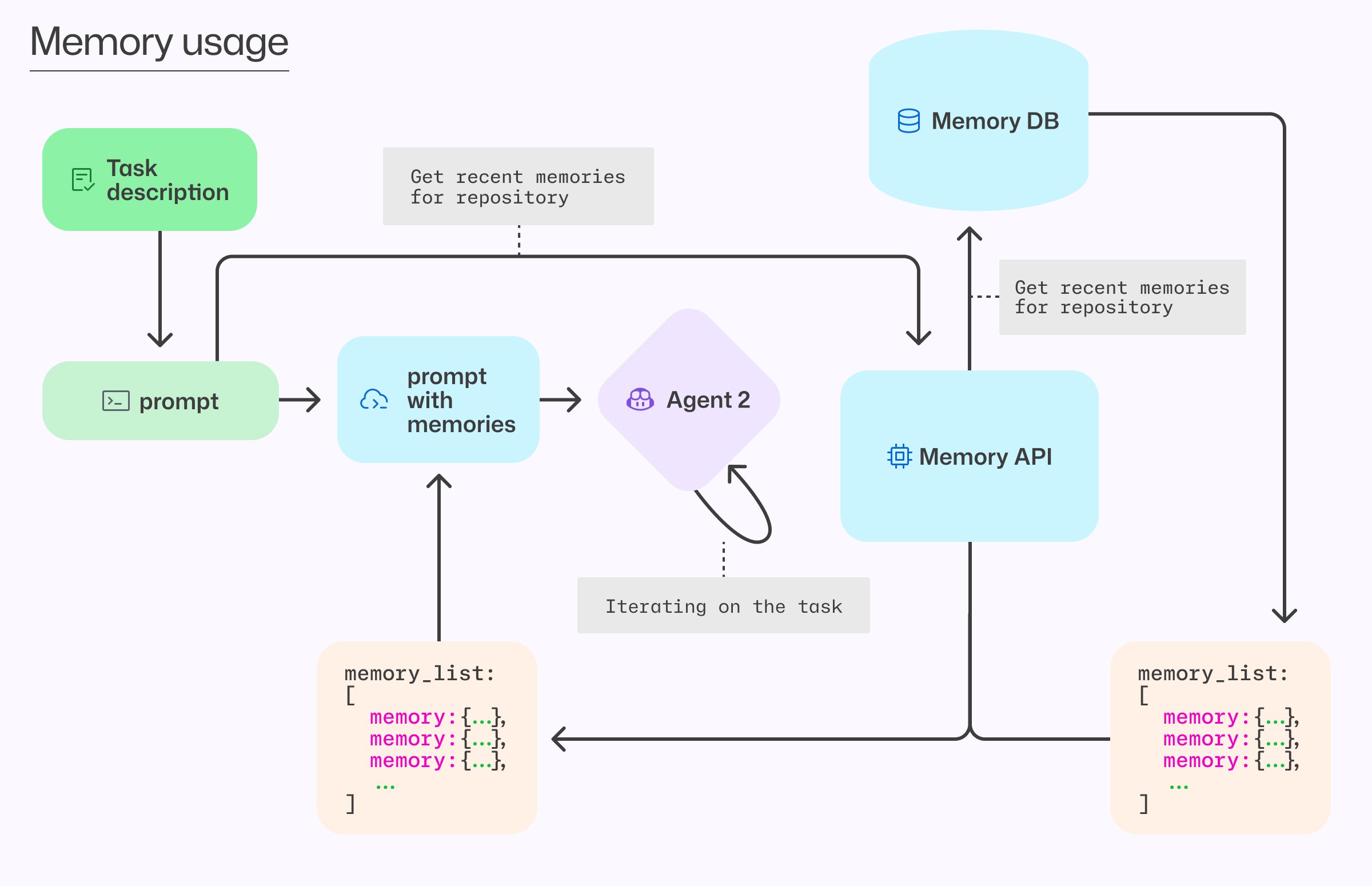 How retrieved memories enrich agent prompts after verification
How retrieved memories enrich agent prompts after verification
Architectural Trade-Offs
This design makes intentional engineering tradeoffs:
| Approach | Advantages | Tradeoffs |
|---|---|---|
| Just-in-Time Verification | Eliminates offline processing; handles codebase volatility | Adds minor latency during agent startup (validated as <50ms in tests) |
| Citation-Based Storage | Enables automatic staleness detection; avoids LLM hallucination risks | Requires precise location tracking; less effective for abstract patterns |
| Repository Scoping | Simplifies security/permissions; aligns with code ownership | Limits cross-repo knowledge transfer |
Real-World Impact
In stress tests:
- Agents successfully detected and corrected 98% of adversarially planted incorrect memories
- Memory usage improved code review precision by 3% and recall by 4%
A/B testing showed measurable developer benefits:
- 7% increase in pull request merge rates when Copilot coding agent used memories
- 2% more actionable code review suggestions with positive developer feedback
Forward-Looking Implications
Currently deployed in Copilot CLI, coding agent, and code review (opt-in), this system enables novel workflows:
- Knowledge transfer: Junior developers benefit from patterns recognized in senior contributors' code
- Cross-agent synergy: A logging convention discovered during review automatically guides debugger behavior
- Proactive maintenance: File synchronization patterns trigger update cascades
Future iterations will explore:
- Conflict resolution for contradictory memories
- Weighted memory prioritization
- Expansion to security and deployment agents
By treating verification as a first-class concern, GitHub's memory system avoids the common pitfalls of AI knowledge bases while enabling truly cumulative learning. As this capability rolls out more broadly, it could fundamentally shift how teams onboard new members and maintain consistency across complex codebases.
Learn about enabling memory in Copilot
Tiferet Gazit is a principal machine learning engineer at GitHub building AI agents for developer productivity.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion