Security researchers at Hacktron exploited a subdomain XSS in Perplexity's Comet AI-powered browser to achieve Universal Cross-Site Scripting (UXSS), granting arbitrary control over the browser. The flaw, rooted in over-permissive external messaging and powerful extension APIs, highlights ongoing risks in composable AI agent systems. Perplexity swiftly patched the issue and awarded a $6,000 bounty.
Hacktron Uncovers UXSS Vulnerability in Perplexity Comet Browser Extension

Composability in modern software stacks enables rapid innovation but also introduces complex vulnerabilities that evade traditional detection. Hacktron researchers demonstrated this by discovering a Universal Cross-Site Scripting (UXSS) flaw in Perplexity's Comet, an AI-powered Chromium-based browser designed for enhanced workflows. The vulnerability chain began with a simple subdomain XSS and escalated to full browser control, exposing the fragility of browser extensions handling sensitive APIs.
The Initial Foothold: Subdomain XSS
Perplexity Comet integrates an AI assistant extension (ID: npclhjbddhklpbnacpjloidibaggcgon) deeply with Chromium. The extension's manifest includes an externally_connectable directive allowing any https://*.perplexity.ai/* subdomain to communicate via chrome.runtime.sendMessage() or chrome.runtime.connect(). This design choice transforms any XSS on a subdomain into a potential extension attack surface.
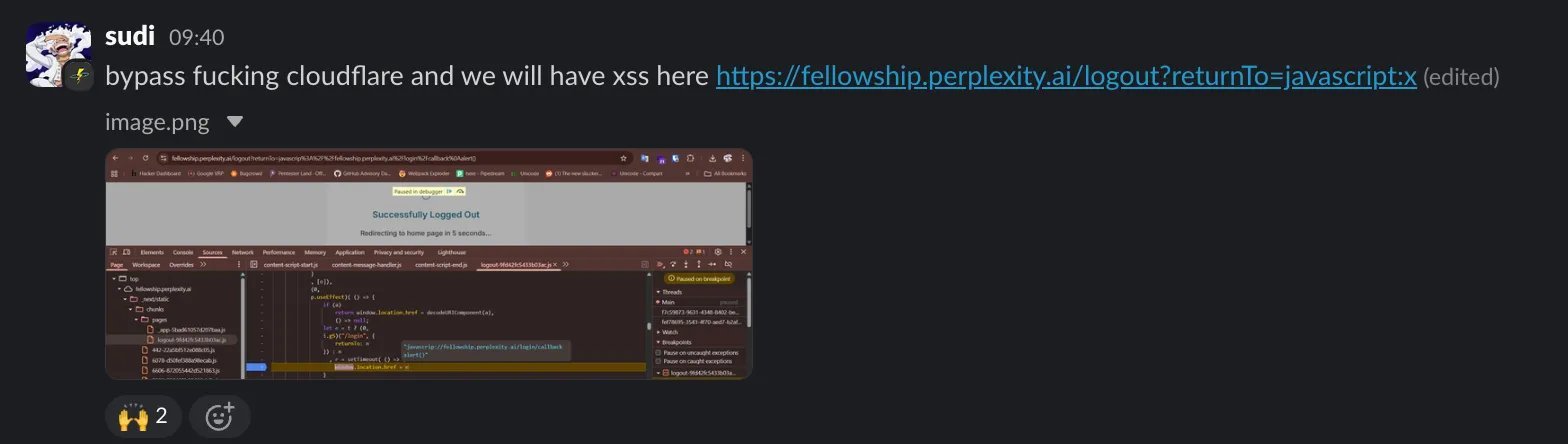
Hacktron's hunt revealed an XSS in https://fellowship.perplexity.ai/logout?returnTo=javascript:x, blocked initially by Cloudflare WAF. Researchers bypassed it with a crafted payload:
java\nscript:\na\n=\n'r")';甲="javascript"+":<img"+" src=x"+" onerror"+="aler"+"t(documen"+"t.domain"+a[2]+">";\ntop["locat"+"ion"]=甲;
This elegant bypass leveraged encoding tricks to evade detection, granting script execution on the subdomain. Source: Hacktron Blog

Escalating to Extension Control and SOP Bypass
With XSS established, attackers can send messages to the extension. Key handlers include RUN_IDLE_TEST, which invokes chrome.debugger.sendCommand('DOMSnapshot.captureSnapshot') and accepts file:// URIs, enabling arbitrary origin DOM snapshots—including local files. A PoC demonstrates fetching Google.com's DOM tree:
chrome.runtime.sendMessage("npclhjbddhklpbnacpjloidibaggcgon", { type: "RUN_IDLE_TEST", message: { url: "https://google.com" }}, res => { console.log("Extension replied:", res);});
Further, CALL_TOOL exposes methods like OpenTab, GetContent, and others via a class handling browser actions. Researchers used it to open mail.gmail.com and extract its content, bypassing Same-Origin Policy (SOP). Attempts to escalate to Remote Code Execution (RCE) via privileged Chrome pages failed, but the control achieved was substantial.
Assistant UXSS: Full Browser Automation
Hacktron's tools flagged a control_browser listener for startAgentFromPerplexity, which opens WebSockets to Perplexity's backend. This triggers task runners performing actions like clicks based on backend selectors. XSS exploitation allows arbitrary URL loading and agent-directed automation, as shown in a PoC reading Gmail and altering Perplexity usernames.
Implications for AI Browser Extensions
This vulnerability underscores risks in AI-driven browser tools. Overly permissive externally_connectable policies, combined with powerful APIs like chrome.debugger and WebSocket integrations, amplify subdomain XSS into UXSS. Developers must tighten origin matching, validate inputs rigorously, and limit API scopes—especially in composable systems where AI agents interact with browsers.
Hacktron's AI agents, while powerful for spotting patterns like DOM XSS sinks, cannot yet autonomously chain complex exploits like Pegasus-style attacks. Human expertise remains essential, though AI accelerates triage.
Perplexity responded rapidly: reported August 19, 2025, patched within 24 hours, and validated by August 21. They awarded Hacktron a $6,000 bounty. Hacktron released free CLI agents (--agent chrome_extension and --agent domxss) to scan for similar issues.
Source attribution: Adapted from Hacktron's detailed case study at https://www.hacktron.ai/blog/perplexity-comet-uxss. Images courtesy of Hacktron.
As AI browsers proliferate, such disclosures drive safer designs, reminding developers that composability's double-edged sword demands vigilant security engineering.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion