Rulebricks introduces Claude Code Guardrails, enabling enterprises to enforce security policies on Claude's coding tools without redeployment.
As AI coding assistants transition from novelty to production infrastructure, enterprises face new governance challenges. Rulebricks' recently open-sourced Claude Code Guardrails addresses a critical gap: real-time policy enforcement for AI-generated tool executions. Unlike static configuration files requiring session restarts, this approach intercepts commands before execution through Claude's PreToolUse hook.
The system operates by routing tool calls through Rulebricks' decision engine, where administrators define rules using visual tables. Policies can range from blocking specific Bash patterns like rm -rf * to complex conditional logic such as "allow node_modules deletion only in CI environments." Changes propagate instantly across all connected Claude instances without redeployment - a significant advantage over JSON-based configurations.
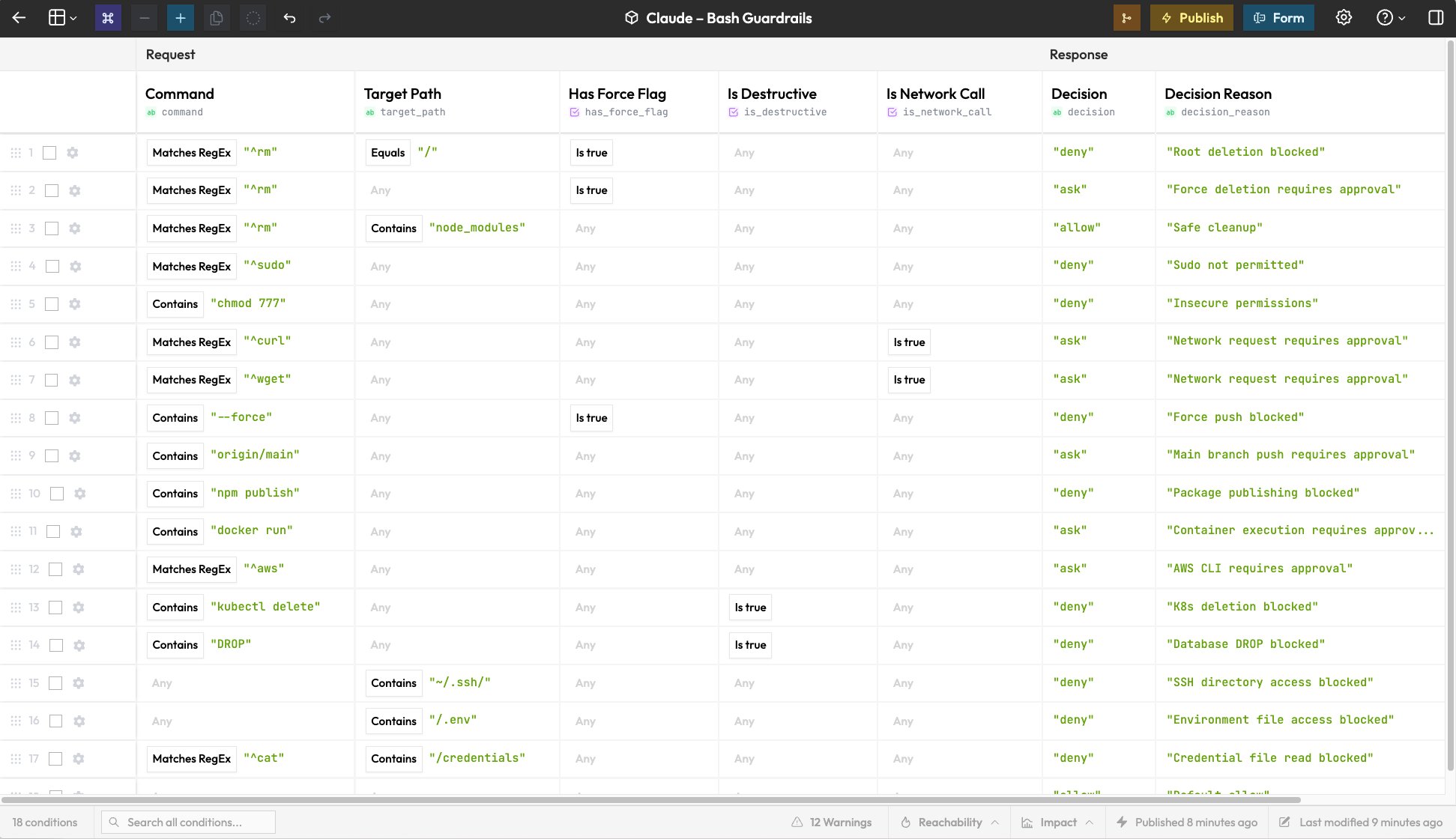
Example rule configuration table for command permissions
Three core guardrail templates cover common scenarios: Bash command restrictions, file operation policies, and MCP server call governance. The setup process involves cloning the GitHub repository, running an installation script, and configuring an API key from Rulebricks.com. Non-technical stakeholders can manage rules through a web interface without touching configuration files.
Audit capabilities represent a key differentiator. Security teams gain visibility into blocked commands with detailed logs showing timestamps, user context, and decision rationale. "The logs reveal patterns you wouldn't otherwise see," notes the documentation, "like which tools get blocked most frequently - invaluable for refining policies."
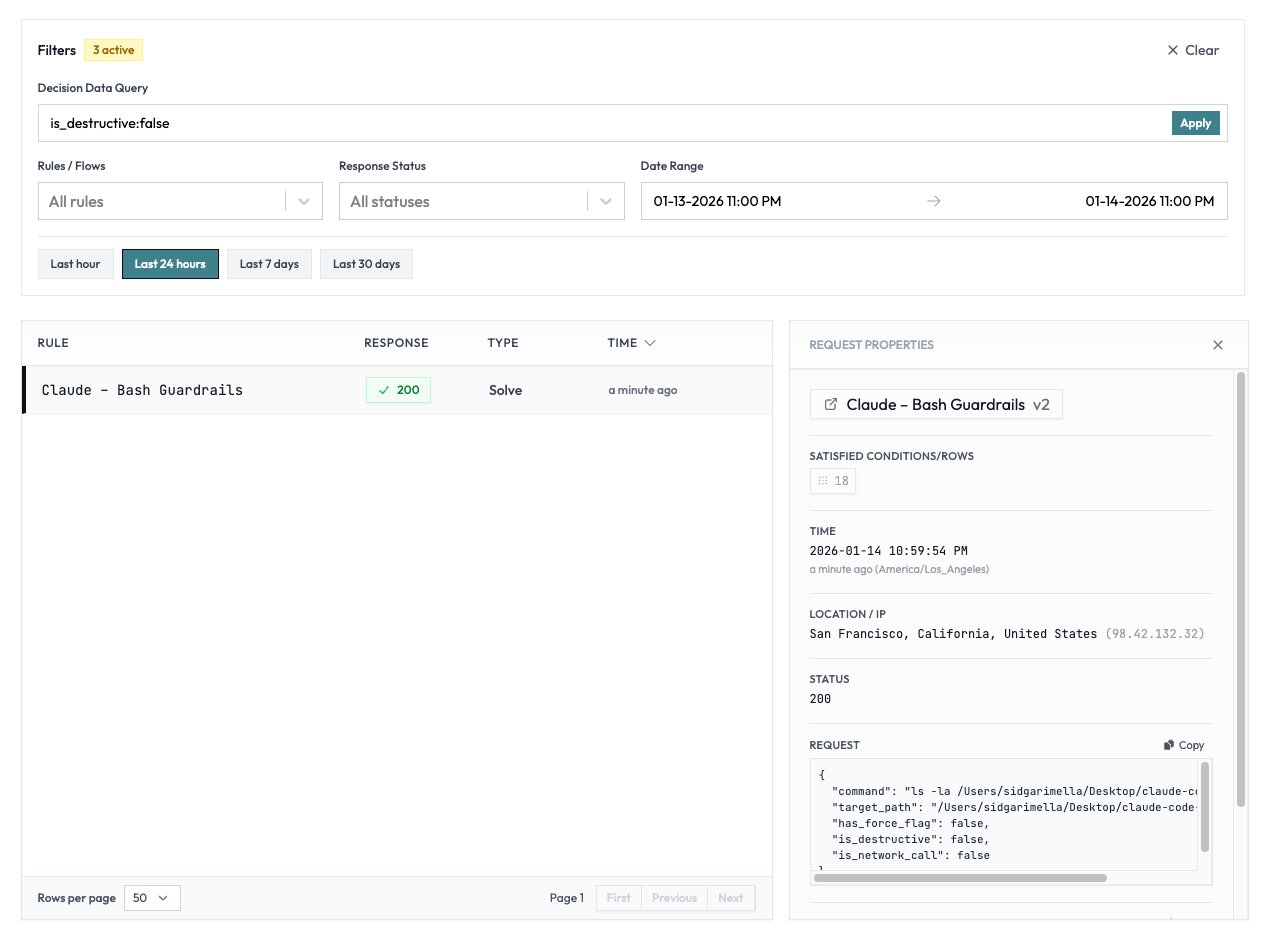
Audit log interface showing blocked command details
Counterperspectives emerge regarding external dependencies. Organizations with basic pattern-matching needs might find native JSON configuration sufficient. Others may hesitate to route tool calls through a third-party service, though Rulebricks addresses this by offering private deployment options and data redaction features before transmission.
This approach reflects broader industry patterns. As LangChain and LlamaIndex mature, middleware for AI tool governance becomes increasingly vital. Rulebricks' model demonstrates how policy enforcement can operate at the tool-call level rather than through post-hoc monitoring - potentially preventing destructive commands before they execute.
The solution doesn't eliminate configuration files entirely. Environment variables in settings.json control API keys and verbose logging, maintaining compatibility with Claude's existing extension model. For removal, developers can delete the hook script and associated settings through a provided one-liner.
As coding assistants handle increasingly privileged operations, solutions bridging security requirements with developer workflow efficiency fill a crucial niche between unrestricted AI tool use and bureaucratic approval processes.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion