Republican senators blocked a vote on Venezuelan sanctions relief, preserving oil export restrictions that contribute to global energy price uncertainty affecting technology operations.
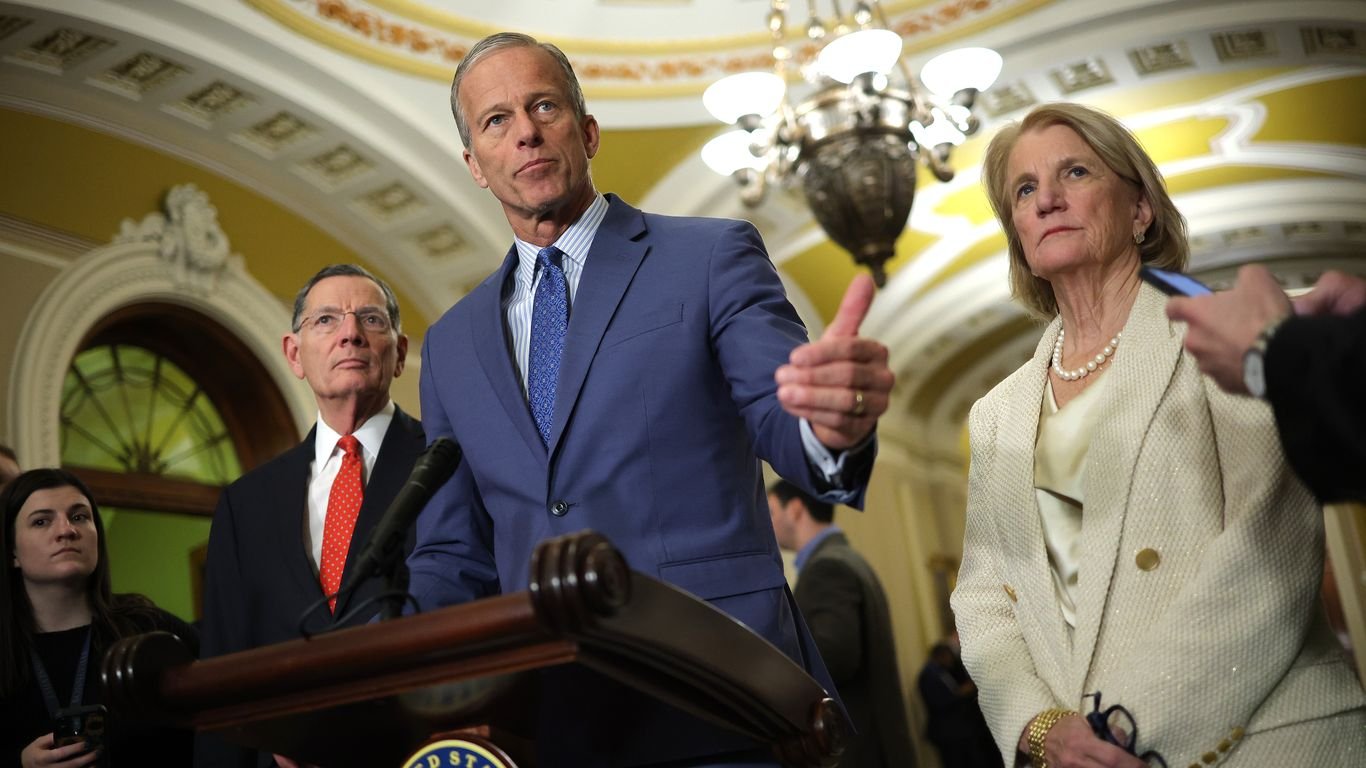
Senate Republicans successfully blocked a last-minute vote on Venezuelan sanctions relief Wednesday, maintaining restrictions on the country's oil exports amid ongoing geopolitical tensions. The maneuver led by Senate Majority Whip John Thune (R-SD) prevents consideration of sanctions easing that would have allowed increased Venezuelan crude shipments to global markets.
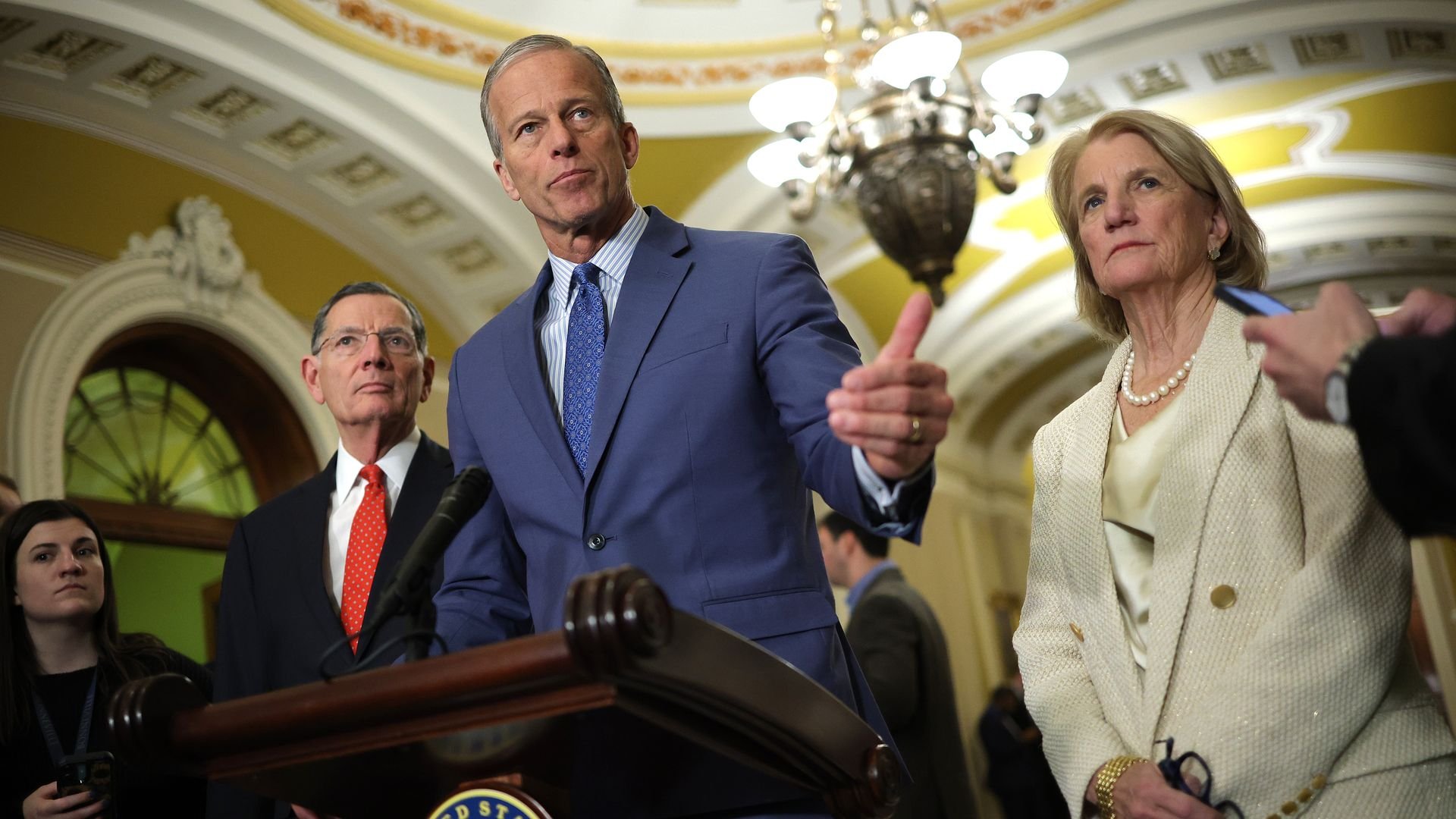
The decision perpetuates constraints on Venezuela's oil production capacity, currently operating at approximately 700,000 barrels per day according to OPEC data - just 25% of its peak output. This comes as global benchmark Brent crude trades at $85.24/barrel, with energy analysts projecting sustained volatility through 2024. The U.S. Energy Information Administration forecasts Brent prices averaging $88/barrel in Q3, citing geopolitical instability as a key risk factor.
For technology enterprises, particularly those operating energy-intensive data centers and manufacturing facilities, sustained oil market volatility translates directly into operational cost uncertainty. Major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud collectively consumed an estimated 90 terawatt-hours of electricity in 2023 - equivalent to the annual power consumption of Portugal. When energy prices increase by 10%, hyperscale data center operators typically see operational cost increases of 3-5% according to Uptime Institute research.
Strategic implications cascade through multiple technology sectors:
- Semiconductor manufacturing: Chip fabrication plants require uninterrupted power, with advanced facilities consuming over 100 megawatt-hours hourly. TSMC and Samsung have both factored energy cost contingencies into 2024 pricing models.
- Logistics and hardware: Elevated fuel costs impact hardware shipment expenses, with Dell and HP reporting 12-15% year-over-year logistics cost increases in Q1 earnings.
- Renewable energy investments: Tech firms are accelerating power purchase agreements for renewable energy, with Meta and Google now covering over 80% of operations with carbon-free energy as a cost hedge.
Market analysts note that while Venezuelan volumes alone wouldn't stabilize oil markets, the Senate action reinforces a fragmented global supply landscape. 'The political calculus around Venezuela maintains a persistent risk premium of $5-7/barrel in current pricing,' notes Rystad Energy senior analyst Jorge León. 'For technology CFOs, this translates to budgeting for energy costs 15-20% above pre-pandemic norms through 2025.'

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion