New research shows Vitamin D and Omega-3 supplements may be significantly more effective at treating depression than traditional antidepressants, with effect sizes up to 4x larger.
Vitamin D & Omega-3 have a larger effect on depression than antidepressants
New research suggests that Vitamin D and Omega-3 supplements may be significantly more effective at treating depression than traditional antidepressants, with effect sizes up to 4x larger.
The Problem with Depression Treatment
Depression affects approximately 1 in 4 people during their lifetime and is the leading source of global disease burden in the mental health category. Traditional antidepressants, while helpful for many, show surprisingly modest effects in clinical trials.
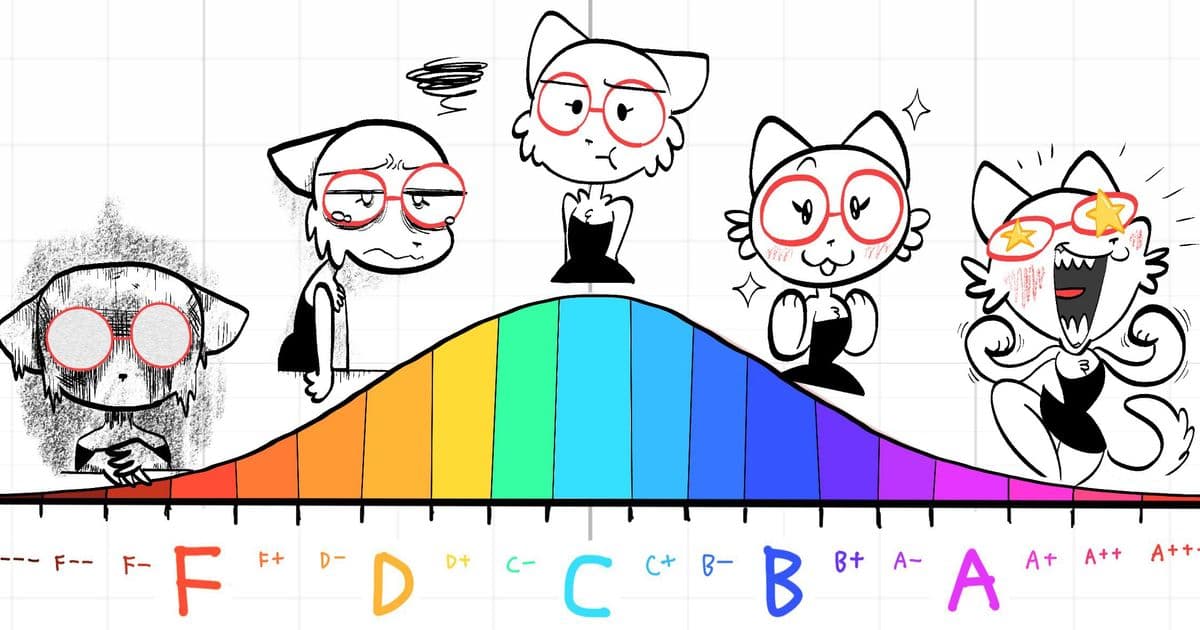
A comprehensive meta-analysis by Cipriani et al. (2018) examined 21 different antidepressants and found that even the most effective one, Amitriptyline, had an effect size of only 0.417 when compared to placebo. This translates to moving someone's mental health from an F to an F+, or from a C to a C+ on a school grade scale.
The Vitamin D Breakthrough
Recent research by Ghaemi et al. (2024) reveals that Vitamin D supplementation shows dramatically better results. Their meta-analysis found that 5000 IU of Vitamin D daily produced an effect size of 1.82 - equivalent to moving someone's mental health from an F to a C–, or from a C to an A–.
Even more remarkably, this effect was observed in people who didn't have Vitamin D deficiency. The study found that 8000 IU showed even better results (effect size 2.04), though with greater uncertainty.
The Omega-3 Advantage
Omega-3 supplements, specifically those with high EPA content, also show superior results. Research by Sublette et al. (2011) and subsequent studies found that 1500 mg daily of Omega-3 supplements with ≥60% EPA content produced an effect size of 0.558 - moving mental health from an F to a D–, or from a C to a B–.
Why These Supplements Work Better
The superior effectiveness likely stems from addressing fundamental nutritional deficiencies that affect brain function. Nearly half of American adults have Vitamin D insufficiency, and many lack adequate Omega-3 fatty acids in their diet.
Practical Recommendations
Based on the research, here are specific recommendations:
Vitamin D: Take 5000 IU daily (10,000 IU if you have darker skin or live in less sunny climates). The official maximum safe dose of 4000 IU is actually below the optimal dose for depression treatment.
Omega-3: Take 1500 mg daily of supplements with ≥60% EPA content. Most official recommendations of 250-500 mg are 3-6 times too low for optimal mental health benefits.
Safety and Accessibility
Both supplements are over-the-counter, inexpensive, and have positive side effects beyond depression treatment. Vitamin D may improve immune response to Covid and influenza, while Omega-3 may enhance cognition.
The Bigger Picture
This research represents a potential paradigm shift in depression treatment. While therapy and antidepressants remain important tools, these supplements offer a low-cost, low-risk option that may be more effective for many people.
As the author notes: "There exist high bang-for-buck ways to reduce depression, which are at least on par with drugs & therapy (possibly 2x to 4x better), that aren't (yet) common knowledge amongst policymakers & the public."
Important Considerations
- Always consult with healthcare providers before starting new supplements, especially if you have kidney stones, are on blood thinners, or are taking other medications
- These supplements can be used alongside existing treatments
- The effect sizes represent averages - individual responses may vary
- More research is ongoing, but current evidence is strong enough to warrant trying these interventions
This research suggests that sometimes the most effective treatments are also the simplest and most accessible. For millions suffering from depression, Vitamin D and Omega-3 supplements may offer hope where traditional treatments have fallen short.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion