A comprehensive look at implementing secure authentication with access/refresh tokens, session management, rate limiting, and clean architecture patterns for production systems.
When building authentication systems for production applications, the devil is in the details. I recently completed a comprehensive authentication system using Express.js and MongoDB that goes beyond basic login functionality to address real-world security concerns and scalability challenges.
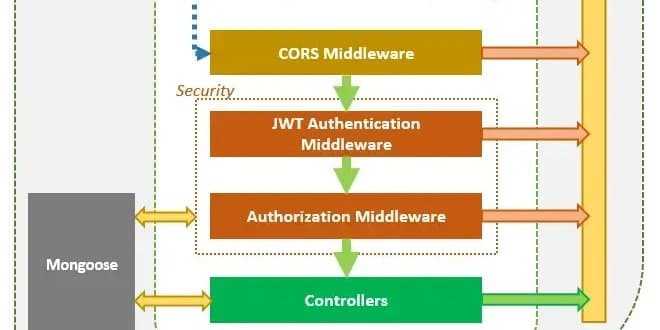
The Architecture Foundation
The system follows clean architecture principles, separating concerns into distinct layers:
- Controllers: Handle HTTP requests and responses
- Services: Contain business logic
- Utils: Reusable helper functions
- Middleware: Request processing and validation
This separation makes the codebase maintainable and testable, crucial for production systems that need to evolve over time.
Token-Based Authentication Strategy
I implemented both access and refresh tokens, a pattern that balances security and user experience:
Access tokens are short-lived (typically 15-30 minutes) and contain user claims. They're sent with each API request for authentication but expire quickly to limit damage if compromised.
Refresh tokens are longer-lived and used to obtain new access tokens without requiring the user to re-authenticate. These are stored securely in the database with proper indexing for quick lookups.
Session Management with MongoDB
Rather than relying solely on JWTs, I implemented session tracking in MongoDB. Each session record includes:
- User ID and session ID
- IP address and user agent
- Creation and last activity timestamps
- Session state (active/invalidated)
This approach enables features like session revocation and concurrent session limits, which are difficult with stateless JWTs alone.
Security Hardening
IP-Based Rate Limiting
To prevent brute force attacks, I implemented rate limiting at 5 attempts per 10 minutes per IP address. This strikes a balance between security and legitimate user access, particularly important for users on shared networks or mobile carriers with NAT.
Validation Middleware
Every input goes through comprehensive validation middleware. This includes:
- Schema validation for request bodies
- Parameter sanitization
- Type checking
- Custom business rule validation
Global Error Handling
A centralized ApiError system ensures consistent error responses across the API. This makes debugging easier and provides a better developer experience for API consumers.
Production Considerations
Automatic Session Invalidation
The system automatically invalidates sessions after periods of inactivity and provides endpoints for manual session termination. This is crucial for security when users might forget to log out on shared devices.
Edge Case Handling
Real-world authentication involves numerous edge cases:
- Token expiration during active sessions
- Concurrent login attempts
- Database connection failures
- Invalid token formats
Each scenario has specific handling to maintain system stability and security.
Testing and Validation
Beyond unit tests for individual components, I implemented integration tests that simulate real authentication flows, including:
- Successful login and token refresh cycles
- Rate limit enforcement
- Session invalidation scenarios
- Error condition handling
Deployment and Monitoring
For production deployment, the system includes:
- Health check endpoints
- Logging for authentication events
- Metrics for monitoring authentication patterns
- Configuration management for environment-specific settings
Lessons Learned
Building this system revealed several insights about real-world authentication:
- Security is layered: No single mechanism provides complete protection
- User experience matters: Overly aggressive security can frustrate legitimate users
- Monitoring is essential: You can't improve what you don't measure
- Edge cases are common: Production systems encounter scenarios you never anticipated
Future Enhancements
The system is designed to be extensible. Potential additions include:
- Multi-factor authentication
- Social login integration
- Passwordless authentication
- Device fingerprinting
- Geographic access controls
Try It Yourself
If you're interested in exploring the implementation details, the complete source code is available on GitHub: authforge-express
I'm particularly interested in feedback on:
- Security improvements
- Performance optimizations
- Additional features that would be valuable in production
- Front-end integration patterns
Authentication is a critical component of most applications, and getting it right requires careful consideration of security, usability, and maintainability. This project represents a solid foundation that can be adapted to various use cases while maintaining security best practices.
What authentication challenges have you faced in your projects? I'd love to hear about your experiences and solutions in the comments.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion