A collaboration between Insilico Medicine and Microsoft demonstrates how the Nach01 foundation model can be deployed on the Microsoft Discovery platform, creating an integrated, AI-native workflow for drug discovery that addresses fragmentation in R&D processes.

The pharmaceutical industry's drug discovery process has long been plagued by fragmented workflows. Scientists typically juggle disparate tools for hypothesis generation, molecular design, and data analysis, making rapid iteration and result reproduction challenging. This fragmentation creates bottlenecks that slow the journey from scientific insight to potential medicine.
A new collaboration between Insilico Medicine, a clinical-stage biotechnology company specializing in generative AI, and Microsoft aims to address this challenge. The partnership demonstrates the deployment of Insilico's Nach01 foundation model on Microsoft Discovery, Microsoft's enterprise agentic platform for AI-accelerated research and development. This integration showcases how third-party models can extend the platform's capabilities to create end-to-end, AI-native workflows spanning biology and chemistry.
The Nach01 Foundation Model: Multimolecular Intelligence
Nach01 represents a specialized approach to foundation models in drug discovery. Unlike large language models trained primarily on text, Nach01 combines multiple architectural techniques to process both chemical structural and spatial data. The model leverages language model architecture alongside a molecular point cloud encoder, enabling it to handle hundreds of diverse tasks in molecular design and prediction.
This multimodal capability allows Nach01 to:
- Predict molecular properties from chemical structures
- Generate novel compounds targeting specific biological sites
- Analyze spatial relationships within molecular structures
- Handle complex chemistry challenges that require understanding both 2D and 3D representations
The model builds upon Insilico's earlier work in textual and 3D spatial representation learning, consolidating these techniques into a unified system designed for the specific demands of drug discovery.
Microsoft Discovery: Enterprise Agentic Platform
Microsoft Discovery serves as the orchestration layer for this integration. Built on Azure, it transforms ad-hoc modeling scripts into managed, repeatable processes. The platform's key capabilities include:
Cognition Engine: An AI-powered system that oversees complex projects, breaking down scientific challenges into traceable, actionable steps. This engine manages task orchestration and ensures workflow integrity.
Knowledge Generation: The platform indexes internal documentation, electronic notebooks, and previous Design Make Test Analyze (DMTA) cycles using graph-based retrieval (GraphRAG). This gives researchers access to organizational knowledge while maintaining context for new experiments.
Scalable Compute Orchestration: Microsoft Discovery leverages Azure ML Workspace to deploy and scale AI models like Nach01 on elastic infrastructure. Compute-intensive workloads such as generative chemistry and large-scale inference execute efficiently across CPU and GPU clusters, with resources scaling based on demand.
Data Connectivity: Integration with Azure's Identity and Access Management (via Microsoft Entra ID) and data services ensures secure, compliant access to organizational data and external resources.
Orchestrating Nach01 in Discovery Workflows
When customers deploy Nach01 on Microsoft Discovery, they gain the ability to compose AI-driven workflows that integrate multiple tools and data sources. The platform's cognition engine enables researchers to configure complex investigations as single, executable workflows.
Practical Workflow Example: Finding a Protein Inhibitor
Consider a drug discovery project aiming to identify a new inhibitor for a specific protein target. Here's how the integrated platform handles each step:
Target Identification: The investigation begins with confirming disease relevance. This might involve knowledge graph queries or literature mining—potentially using other AI services beyond Nach01's scope, all orchestrated through Microsoft Discovery.
Hit Generation: Nach01's generative chemistry capability proposes novel chemical structures predicted to bind the protein's active site. The model generates multiple candidate molecules based on the target's structural information.
Property Prediction: Each proposed molecule undergoes evaluation by Nach01's predictive modules for critical properties like solubility and toxicity (ADMET predictions). This step filters candidates before expensive experimental testing.
Additional Scoring: The workflow can incorporate third-party QSAR models or docking tools, also orchestrated by Microsoft Discovery, providing additional validation layers.
Results Compilation: The platform automatically compiles results and creates visualizations, ranking top candidates as shown in Figure 1.
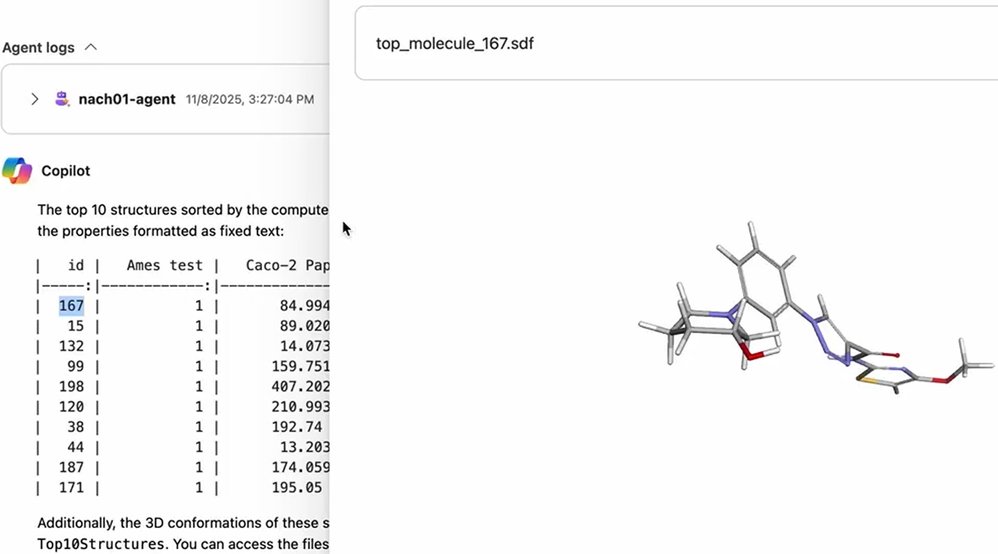
Iteration and Reproducibility
Once configured, the investigation scales based on demand. Microsoft Discovery manages execution, spinning up compute resources as needed and routing data between steps. After execution, researchers review outcomes and can adjust parameters or swap components to refine the investigation.
Crucially, the entire configuration—including model versions, settings, and data sources—is saved in Microsoft Discovery. This ensures reproducibility and enables handoff between teams. A scientist in translational chemistry could reuse an investigation blueprint developed by an AI engineer, applying it to new targets or data with confidence in consistent methodology.
Business Impact: Accelerating the DMTA Cycle
The pharmaceutical industry's Design Make Test Analyze (DMTA) cycle represents the core iterative process of drug discovery. Traditional DMTA cycles can take months or years, with each iteration requiring manual coordination between multiple teams and tools.
The Nach01-Microsoft Discovery integration addresses several critical pain points:
Reduced Fragmentation: By providing a unified platform, researchers avoid context switching between disparate tools. The cognitive engine maintains workflow state, reducing errors from manual data transfer.
Faster Iteration: When suboptimal results emerge, researchers can quickly tweak parameters and rerun investigations. The platform's orchestration ensures changes are tracked and previous runs remain accessible for comparison.
Improved Collaboration: AI specialists and bench scientists work within the same framework. The platform translates complex AI capabilities into actionable workflows that bench scientists can execute without deep technical expertise.
Enhanced Reproducibility: Every experiment's configuration, data sources, and model versions are logged. This addresses a major challenge in computational research where reproducing results often requires reconstructing complex toolchains.
Strategic Implications for Biotech and Pharma
This collaboration represents a broader trend toward AI-native drug discovery, where artificial intelligence becomes deeply integrated into the scientific process rather than serving as an isolated tool. The approach offers several strategic advantages:
Scalability: Organizations can start with specialized models like Nach01 and gradually integrate additional AI capabilities as the platform matures. The cloud-native architecture supports scaling from small pilot projects to enterprise-wide deployments.
Vendor Flexibility: Microsoft Discovery's extensibility allows organizations to choose best-of-breed models for specific tasks rather than being locked into a single vendor's ecosystem. This is particularly important in drug discovery, where different stages may require different AI approaches.
Security and Compliance: By leveraging Azure's enterprise security features, organizations can maintain data governance while using AI models. This is critical for pharmaceutical companies handling sensitive clinical and molecular data.
Cost Management: Elastic compute orchestration means organizations pay only for the resources they use. During periods of intensive generative chemistry work, the platform scales up; during analysis phases, it scales down.
Future Direction: Toward Scientific Superintelligence
As Alex Zhavoronkov, Insilico's Founder and CEO, notes: "From our foundational patents on mutual information in chemistry and biology in 2018 to our deep, ongoing research in multimodality, Insilico has consistently pushed the boundaries of generative AI. While Nach01 is a small, specialized model, its successful launch demonstrates the immense power and scalability of the Microsoft platform. We are now applying these learnings to develop large, highly multimodal models aimed at delivering SOTA and SOTA+ results in every aspect of drug discovery—a critical step toward scientific superintelligence."
The Nach01-Microsoft Discovery integration serves as a proof-of-concept for this vision. It demonstrates that specialized foundation models can be effectively orchestrated within enterprise platforms to create AI-native workflows. As models grow more capable and platforms more sophisticated, the potential exists for increasingly autonomous discovery processes where AI systems propose hypotheses, design experiments, and interpret results with minimal human intervention.
Conclusion: Toward Integrated AI-Native Discovery
The collaboration between Insilico Medicine and Microsoft represents more than a technical integration—it showcases a paradigm shift in how drug discovery can be conducted. By combining Nach01's specialized molecular intelligence with Microsoft Discovery's orchestration capabilities, organizations gain a platform that addresses fragmentation while maintaining the flexibility to incorporate diverse AI models and tools.
For biotechnology and pharmaceutical organizations, this approach offers a path to accelerate innovation while maintaining scientific rigor. Teams can focus on scientific questions rather than technical logistics, iterate more rapidly through the DMTA cycle, and collaborate more effectively across disciplines.
As the industry moves toward AI-native discovery, platforms like Microsoft Discovery, extensible with specialized models like Nach01, provide the foundation for integrating AI as a first-class citizen in the scientific process—from initial hypothesis through experimental validation and beyond.
Learn more about Microsoft Discovery
Explore Insilico Medicine's Nach01 model

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion