Nvidia has reportedly raised its Vera Rubin AI accelerator power target to 2.3kW and memory bandwidth to 22.2TB/s to outperform AMD's upcoming Instinct MI455X, with system-level efficiency and manufacturing benefits offsetting higher power demands.
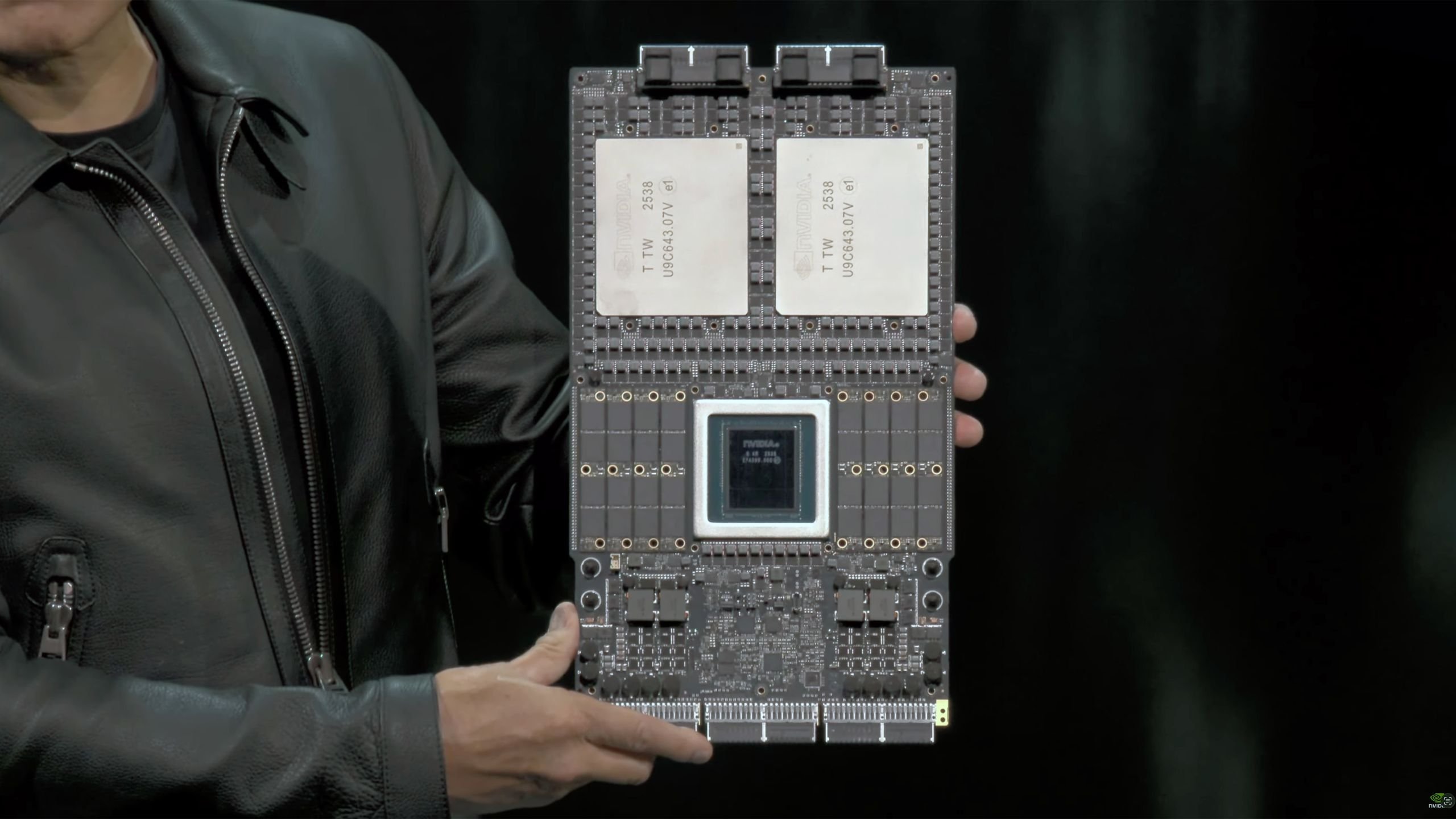
Nvidia has escalated specifications for its upcoming Vera Rubin AI accelerator platform, increasing thermal design power (TDP) from the originally announced 1.8kW to 2.3kW while boosting memory bandwidth to 22.2TB/s according to industry reports. This strategic revision positions Rubin to outperform AMD's competing Instinct MI455X accelerator, projected at 1.7kW TDP, while addressing hyperscaler demands for higher per-node computational density.
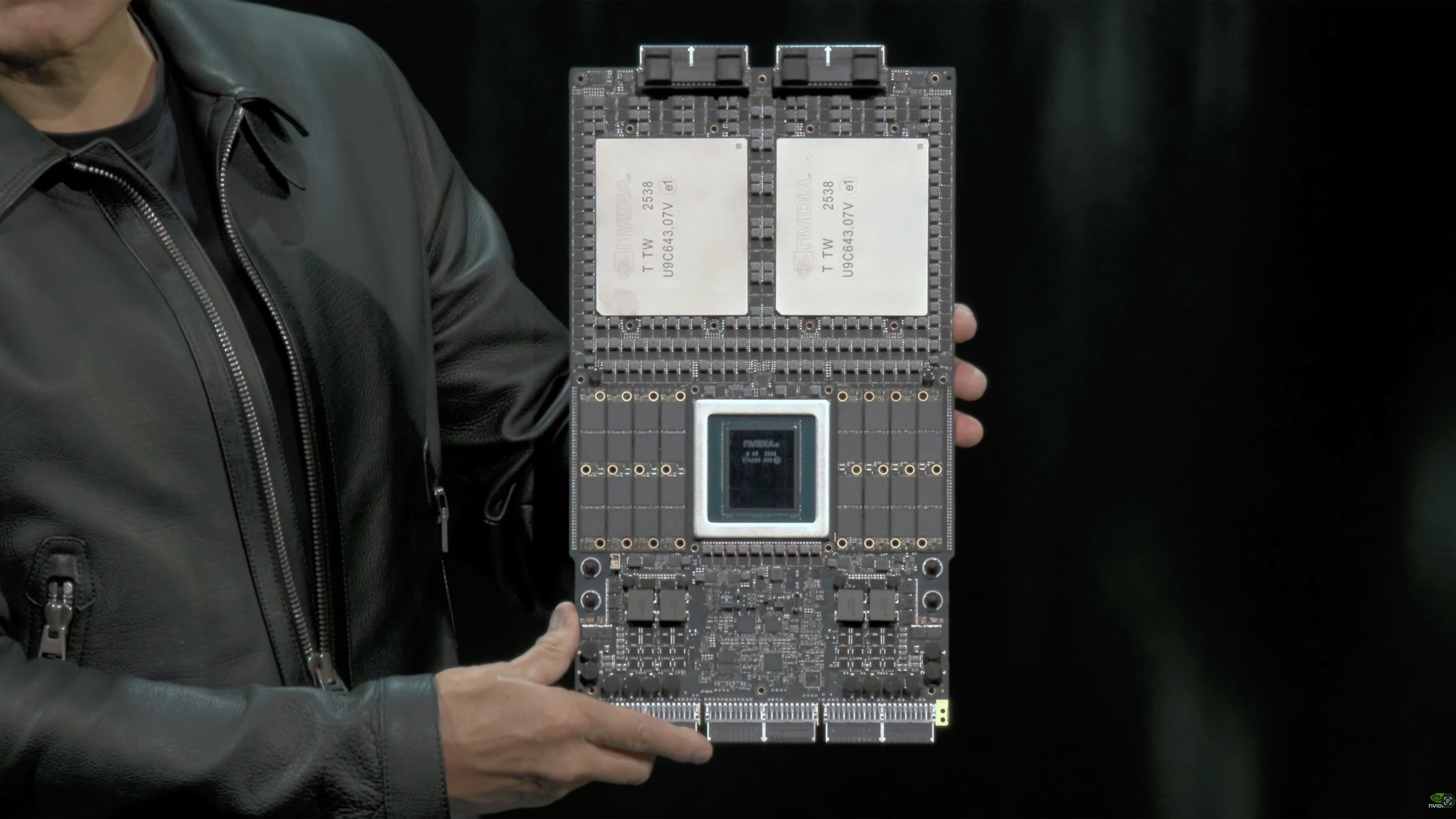
Technical documentation indicates Rubin's HBM4 memory subsystems now operate at accelerated transfer rates, achieving 22.2TB/s bandwidth compared to the initial 13TB/s specification. This 71% bandwidth increase correlates with SemiAnalysis reports of upgraded HBM4 PHY interfaces. The additional 500W power allocation enables multiple performance optimizations: sustained clock frequencies under continuous AI training loads increase by approximately 15%, while memory and NVLink interconnects maintain higher signal integrity margins at aggressive operating points. These enhancements reduce computational throttling during simultaneous memory-compute-interconnect workloads, a critical bottleneck in large language model training.
From a systems perspective, the power increase delivers disproportionate efficiency gains. Hyperscale deployments using Nvidia's VR200 NVL144 rack-scale solution gain approximately 18% more performance per GPU, potentially reducing the number of accelerators required for equivalent workloads. This lowers networking overhead by 12-15% in typical cluster configurations while maintaining total rack power below 100kW thresholds. However, the revised specifications require datacenter operators to provision enhanced cooling infrastructure capable of dissipating 2.3kW per GPU, a 28% increase over previous projections.
Manufacturing benefits emerge from the expanded power envelope, providing 7-9% additional voltage headroom for binning flexibility. This allows Nvidia to salvage chips that would otherwise require core count reductions, potentially improving usable yield by 5-6% without compromising base clocks. Combined with the accelerated HBM4 implementation, these changes position Rubin to outperform AMD's Instinct MI455X by an estimated 25% in FP8 tensor operations while maintaining compatibility with existing Blackwell architecture software stacks.
Market analysis indicates Nvidia's specification adjustments respond directly to AMD's competitive positioning. The Instinct MI455X's 1.7kW TDP and projected 18TB/s memory bandwidth would have narrowed the performance gap with Rubin's original specifications. By increasing power allocation while optimizing memory subsystems, Nvidia maintains a 35% performance-per-watt advantage. Hyperscalers including Google Cloud and Azure have reportedly prioritized per-rack throughput over absolute power efficiency, making Rubin's revised specifications commercially viable despite increased energy requirements. Production validation for the updated design remains on schedule for Q4 2024 shipments.

Anton Shilov is a contributing writer covering semiconductor manufacturing and datacenter technologies.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion